Power plays are those critical moments in limited-overs formats where rules shift to favor aggressive play, allowing batsmen to unleash their full potential while bowlers scramble for control. This leads to exciting moments in the game with big hits, fast runs and great catches
Power play in cricket are special periods where the rules favor the batting team, allowing them to score more runs and play more aggressively. The Cricket fielding position in powerplay has restrictions on where they can place fielders, making it harder for them to stop the batsmen from scoring.
What is power play in cricket?
Cricket can be a really exciting game and one of the things that makes it thrilling is the “power play”. This is a rule that lets the batting team score more runs in a certain number of overs (or deliveries). During this time, the best fielding has to keep more players close to the action, which makes it easier for the batting team to score runs.
The batting team tries to score as many runs as possible during the power play to get a strong start. What exactly is Power Play in cricket? This means fewer fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle, resulting in more runs being scored but also increasing the risk for batsmen.
Cricket power play rules
Mandatory Powerplay: The first 10 overs of the game, with a maximum of two fielders outside the 30-yard circle.
Overs 11-40: A maximum of four fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle.
Overs 41-50: A maximum of five fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle.
These rules are in place to balance the advantage between the batting and fielding teams. The powerplay in cricket adds a new tactical dimension to the game, making it more unpredictable and exciting for fans.
Powerplay was first introduced in 1980-81 in Australia and was renamed by the International Cricket Council (ICC) in 2005. The rules have undergone several changes since then, with the current rules being in place since 2015.
What are power play rules in ODI cricket?
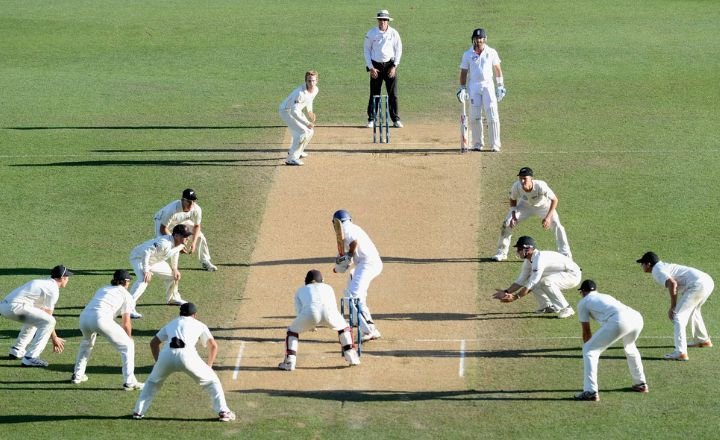

ODI powerplay rules cricket can unlock deeper insights into how matches unfold. Power play in cricket are not just about runs; they transform the dynamics of a match, creating moments that can swing fortunes in an instant. they must balance risk and reward while keeping one eye on victory.
Following odi powerplay rules:
1.Over(1-10)
This is the mandatory powerplay phase, where a maximum of two fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle.
2.Over(11-40)
During this phase, a maximum of four fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle.
3.Over(41-50)
In the final 10 overs, a maximum of five fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle.
Highest runs in ODI power play
| Team A | Team B | Runs |
| Australia | India | 112(10 over) |
| West Indies | India | 114(10 over) |
| New zealand | England | 116(10 over) |
| Australia | New Zealand | 118(10 over) |
| New Zealand | Sri Lanka | 118(8.2 over) |
Highest runs in T20 power play
In the format of T20 cricket, the power play is a crucial phase that can set the tone for the entire match. During this time, only two fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle, creating an environment ripe for aggressive batting. The power play in cricket is a crucial time when the batting team can capitalize on field restrictions to score runs freely.
This initial period allows batsmen to take advantage of fielding restrictions, creating opportunities for explosive scoring. The record for the highest runs scored in a T20 power play showcases the thrilling potential of this format; teams that maximize their output during these overs often set themselves up for victory.
| Team | Runs |
| Australia | 113 |
| South Africa | 102 |
| West Indies | 98 |
| Ireland | 93 |
| England | 89 |
Most Wickets Taker Bowlers in power play
Top wicket-takers understand this pressure well, they channel it into controlled aggression while knowing fully that capturing early wickets can dampen the spirits of opposing teams right from the start. The powerplay in cricket is a thrilling phase that typically allows bowlers to shine.
Among the competition, one bowler has consistently stood out as the most prolific wicket-taker during these crucial overs. This player’s ability to strategize and exploit batting weaknesses under pressure makes them an asset for any team.
| Players | Wickets |
| MA Starc | 214 |
| TA Boult | 212 |
| AU Rashid | 192 |
| K Rabada | 184 |
Conclusion
Powerplay in cricket adds an exciting twist to the game, allowing teams to score quickly and change the match’s direction. During this phase, fielding restrictions create more opportunities for batsmen to hit boundaries, making the game more thrilling for fans.
The strategic use of fielding restrictions during these overs can often turn the tide in a match, making it essential for both batting and bowling sides to adapt.
FAQs
What is a Powerplay in cricket?
A Powerplay is a specific period in limited-overs cricket where fielding restrictions are applied, allowing the batting team to score more runs.
How many Power Plays are there in an ODI match?
In One Day Internationals (ODIs), there are three Power Plays: the first lasts for 10 overs, and the next two each last for 20 overs.
What happens during the first Powerplay?
During the first Powerplay, only two fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle, encouraging aggressive batting.
Are there different rules for T20 matches?
Yes! In T20 matches, there are also three Power Plays: the first lasts for 6 overs with only two fielders outside the circle, while subsequent ones have different restrictions.
Can teams choose when to use their Power Plays?
No, the timing of Power Plays is fixed by the rules of cricket; they occur at set intervals during the match.